Derivative Product Rule With 3 Terms
Leibniz Rule is the rule defined for derivative of the antiderivative. Section 3-4.
Product Rule With 3 Functions Derivatives Calculus Youtube
F x sin3x 2.
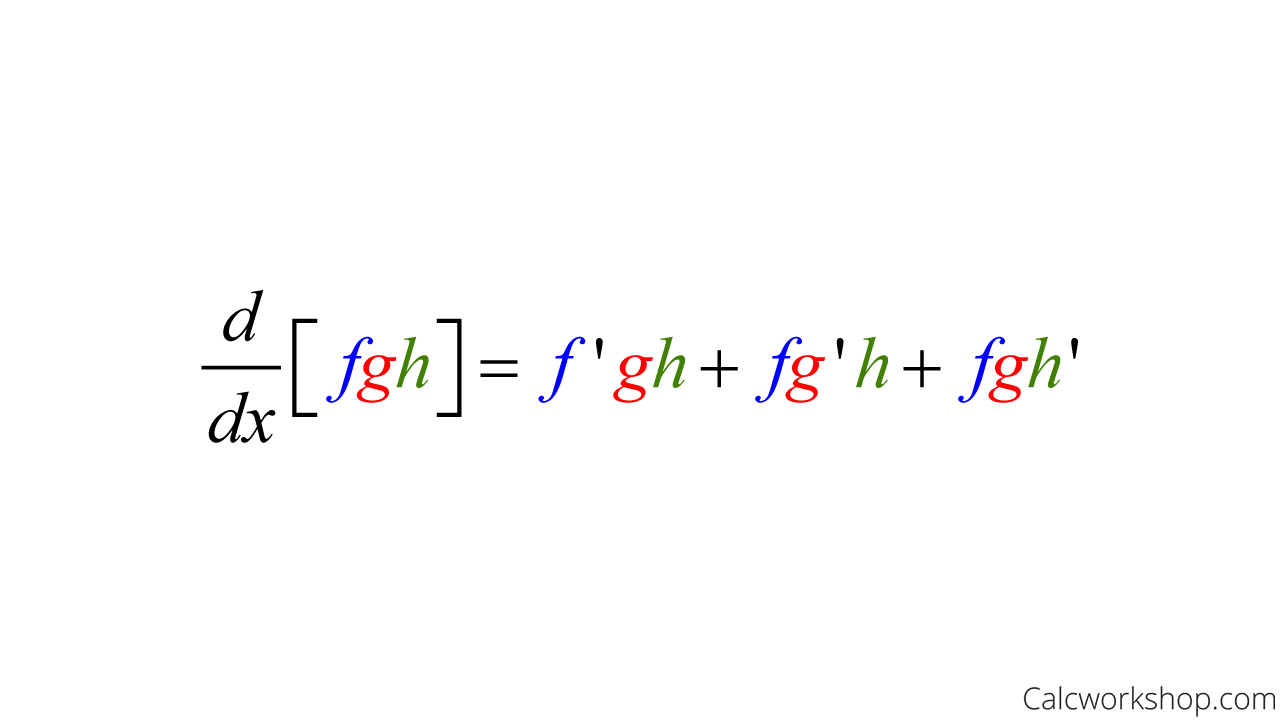
. Lets now work an example or two with the quotient rule. In this case unlike the product rule examples a couple of these functions will require the quotient rule in order to get the derivative. The derivative of sine of x with respect to x weve seen multiple times is cosine of x so times cosine of x.
Basic Derivatives Chain Rule of Derivatives Derivative of the Inverse Function Derivative of Trigonometric Functions etc. By using this site. The above shader implements a step function over the x axis.
Let us discuss these rules one by one with examples. It was the derivative of the outer function with respect to the inner. For the last two however we can avoid.
F x 0 0. The definition of the covariant derivative does not use the metric in space. Find the derivative of x 5.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 30. Free Derivative Product Rule Calculator - Solve derivatives using the product rule method step-by-step Upgrade to Pro Continue to site This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. 10 Evaluating Limits 11 First Order Differential Equations 12 Homogeneous Differential Equations.
As per the Leibniz rule the derivative on the nth order of the product of two functions can be expressed with the help of a formula. Derivative examples Example 1. F x x 3 5x 2 x8.
Like all the differentiation formulas we meet it is based on derivative from first principles. Additional terms may apply. Learn all the Derivative Formulas here.
The derivative of a product of two functions is the first times the derivative of the second plus the second times the derivative of the first Where does this formula come from. Computing the shader derivative of a step function. Y 2x 2 6x2x 3 5x 2.
If x is a variable and is raised to a power n then the derivative of x raised to the power is represented by. This follows from the product rule since the derivative of any constant is zero. This combined with the sum rule for derivatives.
If we have a product like. We want to compute its derivative. Power Rule of Differentiation.
Are given at BYJUS. This is one of the most common rules of derivatives. Product and Quotient Rule.
Then the second derivative at point x 0 fx 0 can indicate the type of that point. However for each metric there is a unique torsion-free covariant derivative called the Levi-Civita connection such that the covariant derivative of the metric is zero. The properties of a derivative imply that depends on the values of u on an arbitrarily small neighborhood of a point.
1 Integrals and Approximations 2 Finding Areas Between Curves 3 The Chain Rule for Derivatives 4 Concavity of Functions 5 Points of Inflection 6 Continuous Functions 7 Cross Sections 8 Integrals 9 What does it mean for a function to be differentiable. For problems 1 6 use the Product Rule or the Quotient Rule to find the derivative of the given function. When applying the chain rule.
Ddxx n nx n-1. Times the derivative of sine of x with respect to x well thats more straightforward a little bit more intuitive. The derivative of a step function would be a Dirac delta function in the continuous domain but in the shaders discrete domain the delta function will be equal to 1 when the step jumps from 0 to 1 and 0 elsewhere.
F x 3x 2 25x10 3x 2 10x1 Example 2. F x cos3x 2 3x 2 cos3x 2 6x Second derivative test. And so there weve applied the chain rule.
When the first derivative of a function is zero at point x 0.
Product Rule For Calculus W Step By Step Examples
Product Rule With 3 Functions Derivatives Calculus Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment